Summary: In this chapter, we will learn how to use the MySQL UPDATE statement to update data in a table.
Introduction to MySQL UPDATE statement
We use the UPDATE statement to update existing data in a table. We can use the UPDATE statement to change column values of a single row, a group of rows, or all rows in a table.
The following illustrates the MySQL UPDATE statement syntax:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| UPDATE table_nameSET column_name1 = expr1, column_name2 = expr2, ...WHERE CONDITIONS; |
First, you specify the table name that you want to update data after the
UPDATE keyword.
Second, the SET clause specifies which column that you want to modify and the new values. To update multiple columns, you use a list comma-separated assignments. You supply the value in each column’s assignment in the form of a literal value, an expression, or a subquery.
Third, you specify which rows will be updated using a condition in the WHERE clause. The WHERE clause is optional. If you omit the WHERE clause, the UPDATE statement will update all rows in the table.
Notice that the WHERE clause is so important that you should not forget. Sometimes, you may want to change just one row; However you forget the WHERE clause and accidentally updates all the rows in the table.
MySQL UPDATE examples
Let’s practice the UPDATE statement with employees tables in the MySQL sample database.
MySQL UPDATE a single column example
In this example, we are going to update the job profile of Tilak Jain to the new post Sr. Software Engineer and his employee id is 1014.
First, we should check current data of Tilak Jain whose employee id is 1014 using the following SELECT statement:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| SELECT firstname, lastname, jobtitleFROM employeesWHERE employeeid = 1014; |
Now, we can update Tilak’s job profile to Sr. Software Engineer using the
UPDATE statement as the following query:
1
2
3
4
5
| UPDATE employeesSET jobtitle = 'Sr. Software Engineer'WHERE employeeid = 1014; |
1 row(s) affected
Because we just want to update one row, we use the WHERE clause to specify the row using the employee number 1014. The SET clause sets the value of the email column to the new email.
In Last, we execute the SELECT statement again to verify the change.
1
2
3
4
5
6
| SELECT firstname, lastname, jobtitleFROM employeesWHERE employeeid = 1014; |
MySQL UPDATE multiple columns
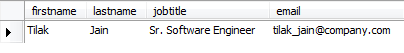
To update values in the multiple columns, you need to specify the assignments in the SET clause. For example, the following statement updates both jobtitle and email columns of employee number 1014:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| UPDATE employeesSET jobtitle = 'Sr. Software Engineer', email = 'tilak_jain@company.com'WHERE employeeid = 1014; |
1 row(s) affected
Let’s execute the SELECT statement to verify the changes.
1
2
3
4
5
6
| SELECT firstname, lastname, jobtitle, emailFROM employeesWHERE employeeid = 1014; |
MySQL UPDATE Warning!
1
2
3
4
| UPDATE employeesSET jobtitle = 'Sr. Software Engineer', email = 'tilak_jain@company.com' |
Be careful when updating records. If we omit the WHERE clause, ALL records will be updated:
1
2
3
4
| SELECT firstname, lastname, jobtitle, emailFROM employees |
WHERE clause is so important that you should not forget. Sometimes, you may want to change just one row; However you forget the WHERE clause and accidentally updates all the rows in the table.
In this chapter, we have learnt how to use MySQL UPDATE statement to update data in a database table.
MySQL INSERT Statement MySQL DELETE
MySQL INSERT Statement MySQL DELETE