Summary: In this chapter, we will learn about MySQL LEFT JOIN clause and how to apply it to query data from two or more database tables.
MySQL LEFT JOIN Introduction
The MySQL LEFT JOIN clause allows you to query data from two or more tables. The LEFT JOIN keyword returns all rows from the left table, with the matching rows in the right table. The result is NULL in the right side when there is no match.
The following statement illustrates the syntax of LEFT JOIN clause:
1
2
3
4
| SELECT column_name(s)FROM table1LEFT JOIN table2ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name; |
In other words, the LEFT JOIN clause allows to select rows from the both left and right tables that are matched, plus all rows from the left table even there is no match found for them in the right table.
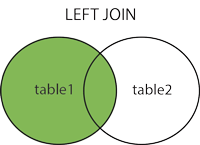
The following Venn diagram helps you visualize how the LEFT JOIN clause works.
MySQL LEFT JOIN Example
Let’s take a look at the employees and branches tables in the sample database.
1
2
3
4
5
6
| SELECT e.firstname, e.lastname, e.jobtitle, b.city, b.countryFROM employees AS eLEFT JOIN branches AS bON e.branchid=b.branchid; |
Above query returns all the rows from the left table (employees), even if there are no matches in the right table (branches).
In this chapter, we have explained the MySQL LEFT JOIN clause and shown you how to apply it to query data from multiple tables.
MySQL INNER JOIN MySQL RIGHT JOIN
MySQL INNER JOIN MySQL RIGHT JOIN