Summary: In this chapter, we will show you how to create new tables in a database using MySQL CREATE TABLE statement.
Creating Tables Using MySQL CREATE TABLE Statement
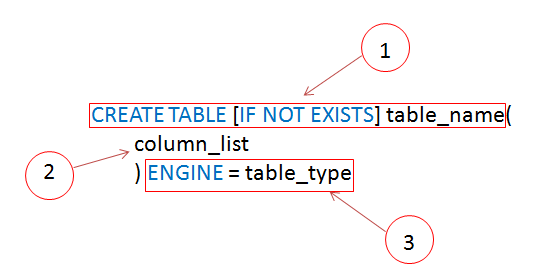
MySQL CREATE TABLE syntax
In order to create a new table within a database, you use the MySQL CREATE TABLE statement. The CREATE TABLE statement is one of the most complex statement in MySQL.
The following illustrates the syntax of the CREATE TABLE statement in the simple form:
Let’s examine the syntax in greater detail:
- First, you specify the name of the table that you want to create after the CREATE TABLE clause. The table name must be unique within a database. The IF NOT EXISTS is an optional part of the statement that allows you to check if the table that you are creating already exists in the database. If this is the case, MySQL will ignore the whole statement and will not create any new table. It is highly recommended that you use IF NOT EXISTS in every CREATE TABLE statement for preventing from an error of creating a new table that already exists.
- Second, you specify a list of columns for the table in the column_list section. Columns are separated by a comma (,). We will show you how to define columns in more detail in the next section.
- Third, you need to specify the storage engine for the table in the engine clause. You can use any storage engine such as InnoDB, MyISAM, HEAP, EXAMPLE, CSV, ARCHIVE, MERGE, FEDERATED or NDBCLUSTER. If you don’t declare the storage engine explicitly, MySQL will use InnoDB by default.
column_list :
To define a column for the table in the CREATE TABLE statement, you use the following syntax:
1
2
3
4
5
| column_name data_type[size] [NOT NULL|NULL] [DEFAULT VALUE] [AUTO_INCREMENT] |
The most important components of the syntax above are:
- The column_name specifies the name of the column. Each column has a specific data type and the size e.g.,VARCHAR(255)
- The NOT NULL or NULL indicates that the column accepts NULL value or not.
- The DEFAULT value is used to specify the default value of the column.
- The AUTO_INCREMENT indicates that the value of the column is increased automatically whenever a new row is inserted into the table. Each table has one and only one AUTO_INCREMENT column.
If you want to set particular columns of the table as the primary key, you use the following syntax:
1
| PRIMARY KEY (col1,col2,...) |
Example of MySQL CREATE TABLE statement
Let’s practice with an example of creating a new table named customers in our sample database as follows:
You can use the CREATE TABLE statement to create the customers table as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS customers ( CustomerID INT(11) AUTO_INCREMENT, CustomerName VARCHAR(45) DEFAULT NULL, ContactName VARCHAR(45) DEFAULT NULL, Address VARCHAR(200) DEFAULT NULL, City VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT NULL, PostalCode VARCHAR(45) DEFAULT NULL, Country VARCHAR(100) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (CustomerID) ); |
Output: 0 row(s) affected
We can verify that table is created or not using MySQL SELECT Query,
1
| SELECT * FROM customers; |
Output: In below image, we can see column names its mean customers table has been created successfully.
In this chapter, we have learnt how to use MySQL CREATE TABLE statement to create a new table in a database.
MySQL Data Types MySQL Primary Key
MySQL Data Types MySQL Primary Key